

| History of OI -> XIII OI 2005/2006 -> Problems |  |
Warehouse
Memory limit: 32 MB
The streets of the New Byte City form a rectangular grid - those running east-west are simply called streets,
while those running north-south are called avenues. To avoid mistakes, we shall call them h-streets and v-streets, respectively.
The v-streets are numbered from 1 to  eastwards. Similarly, the h-streets are numbered from 1 to
eastwards. Similarly, the h-streets are numbered from 1 to  northwards.
Every v-street crosses every h-street and, conversely, every h-street crosses every v-street.
The distance between two consecutive v-streets, as well as between two consecutive h-streets, is exactly one kilometre.
northwards.
Every v-street crosses every h-street and, conversely, every h-street crosses every v-street.
The distance between two consecutive v-streets, as well as between two consecutive h-streets, is exactly one kilometre.

There are  shops in the city,
each one of them is situated at a crossroads.
Byteasar, the merchant, supplies every single one of the
shops in the city,
each one of them is situated at a crossroads.
Byteasar, the merchant, supplies every single one of the  shops,
and furthermore he returns to some of them several times a day with fresh supplies.
Recently he has decided to have a warehouse built, from which the goods would be delivered.
For obvious reasons, it should stand at a crossroads.
The lorry loaded with goods can supply only one shop per course - it leaves the warehouse, delivers to the shop and returns to the warehouse.
The lorry always picks the shortest path from the warehouse to the shop, and the shortest one back (possibly the same one).
The distance between points
shops,
and furthermore he returns to some of them several times a day with fresh supplies.
Recently he has decided to have a warehouse built, from which the goods would be delivered.
For obvious reasons, it should stand at a crossroads.
The lorry loaded with goods can supply only one shop per course - it leaves the warehouse, delivers to the shop and returns to the warehouse.
The lorry always picks the shortest path from the warehouse to the shop, and the shortest one back (possibly the same one).
The distance between points  and
and  equals
equals

Task
Write a programme that:
- reads the locations of shops, as well as the numbers of their daily deliveries, from the standard input
- determines such a warehouse's position that the summary distance of the lorry's daily route is minimal,
- writes the result to the standard output.
Input
The fist line of the standard input contains one integer
 (
( ), the number of shops
in the New Byte City.
), the number of shops
in the New Byte City.
The following  lines contain the shops' descriptions.
The
lines contain the shops' descriptions.
The  -th line contains three integers
-th line contains three integers  ,
,  and
and  (
( ,
,
 ), separated by single spaces.
This triple means that the
), separated by single spaces.
This triple means that the  -th shop lies at the crossing of
-th shop lies at the crossing of
 -th v-street and
-th v-street and  -th h-street
and the lorry delivers goods to this shop
-th h-street
and the lorry delivers goods to this shop  times a day.
times a day.
Output
The first and only line of the standard output should contain two integers
 and
and  , separated by a single space, denoting
the optimal position of the warehouse as the crossroads of the
, separated by a single space, denoting
the optimal position of the warehouse as the crossroads of the  -th v-street
and the
-th v-street
and the  -th h-street.
Should there be many optimal solutions, your programme is to pick one of them arbitrarily.
-th h-street.
Should there be many optimal solutions, your programme is to pick one of them arbitrarily.
3 2 2 1 6 2 1 4 6 1the correct output is:
4 4
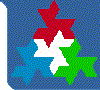
The picture below illustrates the example. The numbered points are the shops. The point S is the optimal position of the warehouse.

Print friendly version

